Are you feeling overwhelmed preparing for the Federal Aviation Administration Part 107 Certification exam? In this article, we have compiled a comprehensive set of FAA Part 107 practice test questions complete with answers to help you prepare better.
Truth be told, you not only need to work hard, you need to work smart.
This free practice test has been developed to simulate the format and content of the actual exam, allowing you to become familiar with the types of questions you’ll encounter.
On a side note, we have helped over 20K pilots earn their Part 107 certification.
Ready to evaluate your readiness for the Part 107 exam? Let me give you a quick overview of the Part 107 knowledge test and what it entails.
What is the Part 107 Knowledge Test?
The FAA Part 107 exam is a test required by the FAA for commercial drone pilots in the US. To get an FAA drone license you must pass the Federal Aviation Administration’s (FAA) Part 107 exam. The exam consists of 60 multiple-choice questions; you must score at least 70% to pass it.

The purpose of the Part 107 Knowledge Test is to verify that drone pilots possess the required knowledge and abilities to operate their drones safely and responsibly.
How to Prepare for the Part 107 Practice Test
The FAA Part 107 exam is a rigorous evaluation that tests commercial drone pilots’ knowledge and comprehension of the rules and operational necessities for drone flights in the United States. Successfully passing the Part 107 exam is a critical step for any drone pilot looking to conduct commercial operations.
To start your journey towards passing the Part 107 exam, we recommend downloading our FREE comprehensive Part 107 Study Guide. This guide is an essential resource for anyone seeking to gain a comprehensive understanding of the knowledge required to pass the exam.

FAA Part 107 Practice Test MCQ Content Overview
The Part 107 Practice Test MCQ covers questions related to:
- Regulations (10 questions)
- Airspace Classification (10 questions)
- Weather (10 questions)
- Loading & Performance (10 questions)
- Operations (20 questions)
Let’s take a look at the sample test questions in each of these categories so you can evaluate yourself thoroughly before the big day.
FAA Part 107 Practice Test Sample Questions
Here you will find a comprehensive collection of topic-wise practice test questions specifically curated to measure your performance and bolster your confidence.
A. FAA Part 107 Practice Test Questions Related to Regulations

1. A professional wildlife photographer operates an sUAS from a moving truck to capture aerial images of migrating birds in remote wetlands. The driver of the truck does not serve any crew member role in the operation. Is this sUAS operation in compliance with 14 CFR Part 107?
A. Compliant with Part 107
B. Not compliant with Part 107
C. Not compliant with state and local traffic laws
2. Remote Pilots are required to complete the following operational area surveillance prior to the sUAS flight:
A. Make a plan to keep non-participants in viewing distance for the whole operation
B. Select an operational area that is populated
C. Keep the operational area free of and at an appropriate distance from all non-participants
3. Personnel at an outdoor concert venue use an sUAS to drop promotional t-shirts and CDs over the audience. Is this sUAS operation in compliance with 14 CFR 107?
A. No, unless authorized by the venue
B. Yes, compliant with Part 107
C. Not compliant with Part 107
4. Which of the following crewmembers must be used during Part 107 sUAS operations?
A. Remote PIC
B. Remote PIC, Visual Observer
C. Remote PIC, Visual Observer, Person manipulating the controls
5. The remote PIC may operate how many sUAS at a time?
A. 5
B. 1
C. No more than 2
6. “Unmanned aircraft” is defined as a device operated
A. during search and rescue operations other than the public
B. without the possibility of direct human intervention from within or on the aircraft
C. for hobby and recreational use when not certified
7. Under what conditions may objects be dropped from the sUAS?
A. if prior permission is received from the FAA
B. in an emergency
C. if precautions are taken to avoid injury or damage to persons or property on the surface
8. Unless otherwise authorized, what is the maximum airspeed at which a person may operate an sUAS below 400 feet?
A. 80 mph
B. 100 mph
C. 200 knots
9. When an ATC clearance has been obtained, no remote PIC may deviate from that clearance, unless that pilot obtains an amended clearance. The one exception to this regulation is
A. an emergency
B. when the clearance states “at pilot’s discretion”
C. if the clearance contains a restriction
10. Under what conditions would a small unmanned aircraft not have to be registered before it is
operated in the United States?
A. When the aircraft has a takeoff weight that is more than .55 pounds but less than 55
pounds, not including fuel and necessary attachments
B. When the aircraft weighs less than .55 pounds on take-off, including everything that is onboard or attached to the aircraft
C. All small unmanned aircraft need to be registered regardless of the weight of the aircraft
before, during, or after the flight
B. FAA Part 107 Practice Test Questions Related to Airspace Classification

11. Which publication contains an explanation of airport signs and markings?
A. Aeronautical Information Manual (AIM)
B. Advisory Circulars (AC)
C. Chart Supplements US
12. Responsibility for collision avoidance in an alert area rests with
A. the controlling agency
B. all pilots
C. Air Traffic Control
13. According to 14 CFR Part 107, how may a Remote Pilot in Command (Remote PIC) operate an unmanned aircraft in Class C airspace?
A. The remote PIC must contact the ATC facility after launching the unmanned aircraft
B. The remote PIC must monitor the ATC frequency from launch to recovery
C. The remote PIC must have prior authorization from the Air Traffic Control (ATC) facility
having jurisdiction over that airspace.
14. When approaching holding lines from the side with the continuous lines, the pilot
A. should not cross the lines without ATC clearance
B. may continue taxiing
C. should continue taxiing until all parts of the aircraft have crossed the lines
15. The lateral dimensions of class D airspace are based on
A. the instrument procedures for which the controlled airspace is established
B. the number of airports that lie within Class D airspace
C. 5 statute miles from the geographical center of the primary airport
16. You have received authorization to operate an sUAS at an airport. When flying the sUAS, the ATC tower instructs you to stay clear of all runways. Which situation would indicate that you are complying with this request?
A. You are on the double solid yellow line side of markings near the runway
B. You are on the double dashed yellow line side of markings near the runway
C. You are over the dashed white lines in the center of the pavement
17. When a manned aircraft is approaching to land at an airport in Class G airspace without an
the operating control tower, the pilot will
A. enter and fly a traffic pattern at 800 feet AGL
B. make all turns to the left unless otherwise indicated
C. fly a left-hand traffic pattern at 800 feet AGL
18. Which is true concerning the blue and magenta colors used to depict airports on Sectional
Aeronautical Charts?
A. Airports with control towers underlying Class B, C, D, and E airspace are shown in blue
B. Aircrafts with control towers underlying Class A, B, and C airspace are shown in blue, Class
D and E airspace are magenta
C. Airports with control towers underlying Class C, D, and E airspace are shown in magenta
19. Under what conditions, if any, may remote pilots fly through a restricted area?
A. With the controlling agency’s authorization
B. When flying on airways with an ATC clearance
C. Regulations do not allow this
20. Which technique should a remote pilot use to scan for traffic?
A. Continuously scan the sky from right to left
B. Systematically focus on different segments of the sky for short intervals
C. Concentrate on relative movement detected in the peripheral vision area
C. FAA Part 107 Practice Test Questions Related to Weather
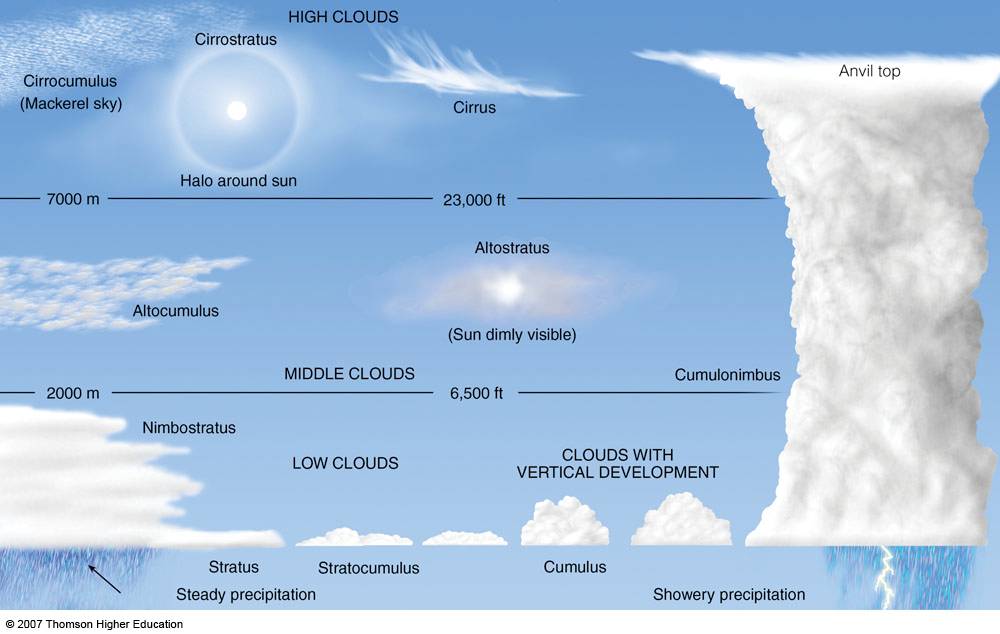
21. The presence of ice pellets at the surface is evidence that there
A. are thunderstorms in the area
B. is a temperature inversion with freezing rain at a higher altitude
C. has been a cold frontal passage
22. The minimum distance from clouds required for sUAS part 107 operations is
A. 500 feet below, 2,000 feet horizontally
B. clear of clouds
C. 500 feet above, 1,000 feet horizontally
23. What is the best way for a remote pilot to determine the likelihood of local fog formation?
A. Monitor the wind conditions to insure the wind speed is not increasing
B. Monitor the barometric pressure to ensure that it is not decreasing
C. Monitor the temperature / dew point spread
24. Which weather phenomenon is always associated with a thunderstorm?
A. Heavy rain
B. Hail
C. Lightning
25. What effect does high-density altitude have on the efficiency of a UA propeller?
A. Density altitude does not affect propeller efficiency
B. Propeller efficiency is increased
C. Propeller efficiency is decreased
26. What are the characteristics of a moist, unstable air mass?
A. Turbulence and showery precipitation
B. Poor visibility and smooth air
C. Haze and smoke
27. In which environment is aircraft structural ice most likely to have the accumulation rate?
A. Cumulus clouds with below-freezing temperatures
B. Freezing rain
C. Freezing drizzle
28. One weather phenomenon which will always occur when flying across a front is a change in
A. wind direction
B. type of precipitation
C. stability of the air mass
29. A stable air mass is most likely to have which characteristic?
A. Showery precipitation
B. Poor surface visibility
C. Turbulent air
30. What is the expected duration of an individual microburst?
A. Two minutes with maximum winds lasting approximately 1 minute
B. One microburst may continue for as long as 2 to 4 hours
C. Seldom longer than 15 minutes from the time the burst strikes the ground until dissipation
D. FAA Part 107 Practice Test Questions Related to Loading & Performance
 Load Factor Graph | Source: FAA
Load Factor Graph | Source: FAA
31. When loading cameras or other equipment on an sUAS, mount the items in a manner that:
A. Does not adversely affect the center of gravity
B. Is visible to the visual observer or other crew members
C. Can be easily removed without the use of tools
32. Which of the following is true regarding the weight and balance of small unmanned aircraft?
A. Operations outside weight and balance limitations may result in loss of control
B. CG cannot change during the flight
C. Lateral CG is not important to small unmanned aircraft operations.
33. A stall occurs when the smooth airflow over the unmanned aircraft’s wing/ propeller(s) is disrupted and the lift reduces rapidly. this is caused when the wing/ propeller (s)
A. exceeds the maximum allowable operating weight
B. exceeds the critical angle of attack
C. exceeds the maximum speed
34. Maximum endurance is obtained at the point of minimum power to maintain the aircraft
A. in a long-range descent
B. in steady, level flight
C. at its slowest possible indicated airspeed
35. When range and economy of operation are the principal goals, the remote pilot must ensure that the sUAS will be operated at the recommended
A. long-range cruise performance
B. specific endurance
C. equivalent airspeed
36. What is the best source for sUAS performance data and information?
A. Pilot report
B. Estimates based upon similar systems
C. Manufacturer publications
37. What effect does an uphill terrain slope have on launch performance?
A. Increases launch distance
B. increase launch speed
C. decreases launch distances
38. When operating an unmanned aircraft, the remote pilot-in-command should consider that the load factor on the wings or rotors may be increased anytime:
A. the CG is shifted rearward to the aft CG limit
B. the gross weight is reduced
C. the aircraft is subjected to maneuvers other than straight and level flight
39. The most critical conditions of launch performance are the result of some combination of high gross weight, altitude, temperature and
A. obstacles surrounding the launch site
B. power plant systems
C. unfavorable wind
40. Before each flight the remote PIC must ensure that:
A. objects carried on the sUAS are secure
B. ATC has granted clearance
C. the site supervisor has approved the flight
E. FAA Part 107 Practice Test Questions Related to Operations

41. Which of the following events is considered a flyaway?
A. Unmanned aircraft does not respond to control inputs and does not execute known lost link
maneuvers
B. Loss of the link between the Remote PIC and the unmanned aircraft
C. Loss of communication link between the Remote PIC and ATC
42. Fatigue can be either
A. physiological or psychological
B. physical or mental
C. acute or chronic
43. A common cause of sUAS flyaway events is
A. frequency interference
B. loss of GPS signals
C. persons standing close to the control station antenna
44. You have just landed at a towered airport and the tower tells you to contact ground control when clear of the runway. You are considered clear of the runway when
A. the aircraft cockpit is clear of the hold line
B. the tail of the aircraft is clear of the runway edge
C. all parts of the aircraft have crossed the hold line
45. Which of the following sources of information should you consult first when determining what
maintenance should be performed on an sUAS or its components
A. Local pilot best practices
B. 14 CFR Part 107
C. Manufacturer guidance
46. What is the best way for the remote PIC to minimize the risk of radio frequency interference during sUAS operations?
A. Never transmit on aviation frequency ranges during flight operations
B. Monitor frequency use with a spectral analyzer
C. Avoid the use of cell phones in the vicinity of the control station
47. Under what condition should the operator of a small unmanned aircraft establish a scheduled
maintenance protocol?
A. When the manufacturer does not provide a maintenance schedule
B. When the FAA requires you to, following an accident
C. Small unmanned aircraft systems do not require maintenance
48. During the preflight inspection who is responsible for determining whether the aircraft is safe for flight?
A. The owner or operator
B. The remote pilot-in-command
C. The certificate mechanic who performed the annual inspection
49. Which would most likely result in hyperventilation
A. The excessive consumption of alcohol
B. Emotional tension, anxiety, or fear
C. An extremely slow rate of breathing and insufficient oxygen
50. Upon GPS signal loss, the remote Pilot should immediately
A. contact ATC and declare an emergency
B. perform the planned lost link contingency procedure
C. operate the sUAS normally, noting to account for any mode or control changes that occur if
GPS is lost
51. After landing at a tower-controlled airport, a pilot should contact ground control
A. when advised by the tower
B. prior to turning off the runway
C. after reaching a taxiway that leads directly to the parking area
52. What action should the remote PIC take upon GPS signal loss?
A. Perform the planned flyaway emergency procedure
B. Follow normal sUAS operational procedure, noting any mode or control changes that
normally occur if GPS is lost.
C. Land the unmanned aircraft immediately prior to loss of control
53. Which will almost always affect your ability to fly?
A. Prescription analgesics and antihistamines
B. Over-the-counter analgesics and antihistamines
C. Antibiotics and anesthetic drugs
54. What antidotal phrase can help reverse the hazardous attitude of “anti-authority”?
A. Rules do not apply to this situation
B. I know what I am doing
C. Follow the rules
55. Which of the following lithium batteries should not be used
A. A battery with a bulge on one of the sides of its case
B. A partially discharged battery that is warm from recent prior use
C. A new battery that has only been charged once, several charging cycles are required prior
to normal use.
56. The responsibility for ensuring that an sUAS is maintained in an airworthy condition is primarily that of the
A. Owner or operator
B. Remote pilot-in-command
C. mechanic who performs the work
57. When flying HAWK N666CB, the proper phraseology for initial contact with Whitted ATC Tower is
A. Whitted, HAWK SIX SIX SIX CEE BEE requesting to operate within Class D, west of the
field.
B. Whitted Tower, HAWK SIX SIX SIX CHARLIE BRAVO five NM west of the airport, request
permission to enter Class D airspace for unmanned aircraft operations below four hundred
AGL, three NM west of the airport
C. Whitted Tower, Triple Six Charlie Bravo, five NM west, operating in Class D below four
hundred AGL west of the airport
58. Who is responsible for determining whether a pilot is fit to fly for a particular flight even though he or she holds a current medical certificate
A. The FAA
B. The medical examiner
C. The Pilot
59. Fatigue can be recognized
A. as being in an impaired state
B. easily by an experienced pilot
C. by an ability to overcome sleep deprivation
60. What action should be taken by the Remote PIC during an sUAS flyaway event?
A. Immediately notify any/all crewmembers, bystanders, and ATC (if applicable)
B. Immediately notify the NTSB
C. Immediately notify any/all crewmembers, local law enforcement personnel, and bystanders
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens if I fail the Part 107 Exam?
If you fail the Part 107 test, you can retake the exam. There is no set limit on the number of times you can retake it. To retake the test, you will need to wait 14 days and pay the $175 testing fee again.
How many questions are on the Part 107 exam?
There are 60 questions to answer in 120 minutes.
What score do I need to pass the Part 107 exam?
You need to score a minimum of 70% to pass the exam.


![FAA Part 107 Practice Test [60 MCQs With Answers]](https://marketing-staging.thedroneu.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Practice-Part-107-Questions-1024x576.png)



Add Your Comment